University Initiatives
We will introduce some of the unique initiatives that have been adopted by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Unique initiatives adopted by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology selects and supports outstanding initiatives that are distinctive and unique in a competitive environment across national, public and private universities, in order to further promote university reform efforts at each university. We would like to introduce some of the distinctive educational reform efforts of our university that have been selected so far.
Unique initiatives adopted by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology selects and supports outstanding initiatives that are distinctive and unique in a competitive environment across national, public and private universities, in order to further promote university reform efforts at each university. We would like to introduce some of the distinctive educational reform efforts of our university that have been selected so far.
-
Education and Learning Support for a "Student-Centered University" -Efforts of the Education and Learning Support Center-
-
2003 Distinctive University Education Support Program (University-wide)
-
The Center for Education and Learning Support (Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning), which opened in 2000, is working to build a comprehensive learning support system by primarily working to increase students' motivation to learn and improve faculty teaching methods.
-
Enhancing and developing essential facts education in Law School
-
2004 Program for Promoting Education Law School and Other Professional Graduate School
* Law School (currently: Professional Graduate School Education Promotion Program)In order to study how education on "essential facts," which is essential for the practice of civil litigation, should be conducted and improved at Law School, the "Law School Essential Facts Education Research Institute" was established. The results of this research are disseminated to Law School and law-related institutions nationwide.
-
Developing teaching careers through collaboration with schools - Teacher training project in collaboration with local boards of education, schools, and affiliated schools -
-
2005: Promotion Program for the Training of Highly Qualified Teachers (University-wide) (Currently: Promotion Program Professional Graduate School Education)
The project aims to train teachers with practical leadership skills who can respond to new challenges in schools by collaborating with local public schools and boards of education through programs such as "school internships," "on-the-job training," "educational practice courses," and "mobile consultation services for developmental disorders and school maladjustment."
-
A comprehensive support system for students to obtain qualifications
-
2005: Distinctive University Education Support Program ※Junior college
In addition to acquiring practical skills that will enable students to contribute to society, the school also aims to develop students who can improve themselves through independent and continuous learning and contribute to society. Through this initiative, many students have taken on the challenge of obtaining qualifications, and on average each student has taken 4-5 exams and obtained two qualifications.
-
Practical English education using experience-based learning - Aiming to develop women who are socially and internationally minded -
-
2006 Distinctive University Education Support Program ※Junior college
In the English curriculum, we place importance on experiential learning in English education, and have had overseas language training programs since the school's opening, with one in two students having participated to date. Even for students who do not participate in the overseas language training programs, we provide a place where they can have a simulated study abroad experience while remaining in Japan.
-
Aiming to become a cutting-edge international center for cooperative education
(Professor Kazuhiko Sekita: Creating an international network for cooperative education) -
2006 University Education Internationalization Promotion Program (University-wide)
This initiative aims to build a practical research base in Japan for Cooperative/Collaborative Learning, which is attracting attention as an effective teaching method in university education. We are promoting the creation of a network with collaborative education researchers around the world.
-
Economics education in the age of globalization: Learning economics in English opens up new possibilities for the future
-
2007 Distinctive University Education Support Program ※ Faculty of Economics
This initiative is centered on the Faculty of Faculty of Economics' "International Program (IP)," which teaches economics in English. It provides opportunities for students to acquire the academic English necessary to take economics lectures in English, link with specialized subjects, and international exchange.
-
A WBT (Web Based Training) system that allows students to collaboratively create questions - Promoting autonomous learning using ICT (Information and Communication Technology) -
-
2007 Contemporary Educational Needs Initiative Support Program (University-wide)
By having students use computers to create questions related to their course subjects, they establish a style of self-researching and learning. They then make these questions available to students in their same group (on the Web), and students can post comments to each other, thereby cultivating communication skills and solidifying their understanding.
-
Diverse international exchange and training programs for young researchers
(Associate Professor Manabu Asai: Analysis of financial markets using realized volatility) -
2007 University Education Internationalization Promotion Program (University-wide)
A collaborative project with professors from the University of Western Australia and the Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, leveraging an international network to analyze financial markets using cutting-edge methods.
-
Diverse international exchange and training programs for young researchers
(Professor Junichi Kanzaka: Comparative economic analysis of Japan and the European Community of Villages) -
2008 University Education Internationalization Promotion Program (University-wide)
Village communities in Japan have effectively managed water resources, which are essential for agricultural work, in a variety of ways. In this project, through joint research with overseas researchers of agricultural history, we will first clarify the "wisdom" behind this traditional community water resources management using an economic model. We will then clarify the characteristics of water resources management in Japan through a comparison with the functions of village communities based on the European open field system.
-
Collaboration between universities, citizens, and the government aimed at establishing Hachioji Future Studies and enhancing practical activities (joint application by 14 schools, with Tokyo Tech as the representative school)
-
2008 Strategic University Cooperation Support Program for Enhancing University Education
The "Advanced University Collaboration and Practical Activities among Universities, Citizens, and Government Aiming to Establish Hachioji Future Studies" project, which was proposed by Tokyo National College of Technology as the representative school, was adopted for the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology's 2008 "Strategic University Collaboration Support Project." This initiative involves collaboration between 14 universities, junior colleges, and technical colleges in the Hachioji area, with faculty and students participating and challenging themselves across universities in research projects that take into account the characteristics and issues of the area. The results and methods that emerge from this activity are called "Hachioji Future Studies," and the aim is to form the foundation for a "knowledge hub" in Hachioji. The project period is three years, from fiscal year 20 to 22.
"Hachioji Future Studies" Participating Schools
Partner universities: Kyorin University, Kogakuin University, Soka University, Takushoku University, Tama Art University, Tokyo Kasei Gakuin University, Tokyo University of Technology, Tokyo Junshin Women's University, Tokyo Zokei University, Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, Meisei University, Soka Women's Junior College, Yamano College of Soka Women’s College and Beauty
Representative school: Tokyo National College of Technology
-
Initiatives to improve career path employment rates and satisfaction by using portfolios, etc.
-
2009 University Education and Student Support Promotion Project [Theme B]
Student Support Promotion Program (comprehensive student support, including strengthening job-hunting support) *University-wideOne of the objectives of the bachelor's degree program is to "ensure that students acquire the skills necessary to succeed in society." As an indicator of the results, our university has placed emphasis on the career path decision status of students at the time of graduation and has been working to improve it. However, the career and employment environment surrounding students today is tough. In order to overcome this situation and improve the rate of students deciding on their career path at graduation, this program aims to strengthen the university's career formation support, career and employment consultation, and the provision of job and employment information. It has already been decided to introduce a career portfolio system from the second half of 2009, giving students an opportunity to think about their future and career path from their first year, and by accumulating and utilizing various histories, we will support students in designing their own future. Furthermore, in order to improve the career and employment support that becomes more diverse as students progress through the academic year, we will improve individual interviews with students by faculty and staff, and build a system to continuously provide encouragement and advice.
-
A project to expand knowledge through collaboration between universities in Hokkaido, Kanto, Tokai, and Kinki
-
2009: Strategic University Cooperation Support Program for Enhancing University Education (Comprehensive Cooperation Type) *University-wide
This initiative is aimed at further improving the quality of university education and cultivating talented people for society, as it brings together six universities with a history of educational collaboration through the NPO CCC-TIES Consortium (representative school: Tezukayama University, partner schools: Soka University, Sapporo University, Meiji Pharmaceutical University, Aichi Gakuin University, and Nagoya Gakuin University), with the aim of enriching university education and expanding the "sphere of knowledge" (area of knowledge) in society through educational collaboration, sharing, and disclosure.
To this end, we aim to expand the "knowledge domain" (area of knowledge) by collaborating, sharing, and opening up education, in order to improve the quality of university education and develop human resources, through the following projects: 1. Sharing educational resources of partner universities (sharing educational content and promoting credit-transferable and complementary lectures, reusing lecture videos, and encouraging student exchange between universities); 2. Quality assurance of education (substantiating bachelor's degree skills and researching quality assurance of education); 3. Enhancing FD through university collaboration (ensuring objectivity in class evaluations, sharing educational results, and changing faculty awareness); and 4. Opening up education and expanding the scope of knowledge (public opening of lectures, high school-university collaboration, lifelong education, and international exchange). We also support the revitalization of the local economy and culture, and work together to fulfill the social responsibilities of the university as a base of knowledge.
-
Establishment of a learning support system to support first-year and introductory education
-
2009 University Education and Student Support Promotion Project [Theme A]
University Education Promotion Program (Enhancing quality assurance efforts in universities) *University-wideIn this initiative, the Center for Education and Learning Support (Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning) will work with the Center for General Subject Management and each faculty to implement the Curriculum-Linked Study Skills Training (ASTAC) and a special support program for students with poor academic performance (the Oasis Program). In ASTAC, several subjects are selected each semester from the regular curriculum (general subjects and introductory specialized subjects for the faculty), and the instructors of the subjects work with Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning to provide study skills training through class assignments, while in the Oasis Program, individual instruction on study skills is provided to students recommended by advisors. In addition, broadcast materials (mini-lessons) will be prepared to teach the study skills that students are expected to acquire, and information will be provided to all students on campus using area one-segment broadcasting (utilizing communication technology).
Through this initiative, we aim to (1) improve overall grades (GPA) by improving study skills, (2) reduce students with poor grades primarily due to lack of study skills, and (3) improve motivation to learn and self-image through the effective use of study skills. In addition, we will promote FD initiatives, such as clarifying lesson plans through discussion of skill training issues with subject teachers and jointly creating syllabi. Furthermore, we will build a peer support system for learning support centered around those with experience as SAs in the basic seminars, and promote educational exchange between students.
-
Linking academia, the world, and work to foster employability
Creating a curriculum that connects specialized education with employability and individual learning maps -
2010 University Student Employment Skills Development Support Project ※ Faculty of Economics
In order to develop employability, we believe that merely rearranging the subject groups is not enough, and that it is essential to devise an educational curriculum that is based on the learner's perspective. To this end, we will implement the following initiatives.
Initiative 1: Establishment of a new course, "Social Contribution and Economics" (2nd semester of first year), in collaboration with corporate personnel
Initiative 2: Introduction of "tentative career decision" and "career preference survey/employability assessment test" in the second year
Initiative 3: Development of an individual learning map for careers (My Map)
Initiative 4: Implementing overseas career training and expanding domestic and international internships
In the second semester of their first year, students take "Social Contribution and Economics" (Initiative 1) to develop a view of careers and work, and to learn about the usefulness of economics in society through concrete examples. In this course, students clarify the selection criteria for the course system that is set up from the second year, and learn about the link between specialized subjects in the Faculty of Faculty of Economics and work. In their second year, they make a "tentative career decision" and take a "career preference survey and employability test" (Initiative 2). Students understand their own individuality and current abilities, and become aware of the skills required for their desired career path.
In faculty development activities, faculty members will share the importance of developing employability skills with each other through revised Curriculum Check Lists (CCLs). In addition, they will create Curriculum Maps (CMs) that link specialized education with employability skills. Meanwhile, students will receive advice from faculty members based on the CCLs and CMs and will create My Maps (Initiative 3) with reference to their test results. In the process, students will envision the courses they will take until graduation, taking into account the skills necessary for their desired career paths.
From the second semester of their second year, students take "exercises" that form the core of their specialized subjects. During the spring and summer holidays of each year, students participate in overseas career training or domestic or international internships (Initiative 4) to experience how the knowledge they learned in "Social Contribution and Economics" and specialized subjects is being used on the front lines of society. In the first semester of their third year, they decide on their career path. At the time of graduation, students can use My Map to check for themselves the results of their learning, including the specific abilities and skills required of professionals.
Through this initiative, we aim to develop the employability skills that will lead to students' social and professional independence, and to achieve the educational goals of the Faculty of Faculty of Economics.
-
Promoting independent learning using a common platform system for developing bachelor's degree skills
-
2012 Inter-University Collaborative Education Promotion Project *All universities
Partner School Name
Chitose Institute of Science and Technology (representative school), Soka University, Yamanashi University, Ehime University, Saga University, Hokusei Gakuen University, Aichi University, Sakura no Seibo Junior College
Partner Institutions
Japan Society for Remedial Education, University e-Learning Council, Japan Society for Information Studies Education
Initiative period
2012 to 2016
Overview of the collaboration
Eight universities, both national and private, science and humanities, undergraduate and junior college, and academic societies, which are aware of the issue of quality assurance in bachelor's degree skills, will work together to share common foundational educational elements related to bachelor's degree skills (textbooks, model syllabus, achievement tests) on a common cloud-based infrastructure system. Based on this, 1) the learning and learning perspective characteristics of students at the admission stage of each university will be grasped and shared, and a learning support program for first-year students that should be implemented at each university will be implemented, and 2) a common career-related learning support program in which weak points based on common achievement tests in response to societal demands will be independently studied through e-learning will be implemented. 3) A high-quality educational program will be developed while sharing the distinctive educational methods of each university through FD and SD between universities, with the aim of cultivating autonomous human resources who can solve problems by themselves by skillfully utilizing basic knowledge and skills. Furthermore, a series of initiatives will be carried out in collaboration with academic societies to create versatile learning contents and methods that can be used at other universities and in local communities, contributing to improving the quality of higher education in Japan in the age of universality.
-
Global Human Resource Development Promotion Project
-
2012 Global Human Resource Development Promotion Project (Characteristics Type) *University-wide
In this modern age of accelerating globalization, this initiative defines human resources who possess the following qualities as global human resources and aims to develop such human resources.
- Foreign language proficiency equivalent to TOEFL iBT80, broad education and deep expertise (wisdom)
- Practical intercultural understanding gained through overseas study experiences and the courage to actively participate in the international community
- The idea of coexistence (compassion) is cultivated through the study of university courses that teach the history and educational philosophy of our university.
In April 2010, our university formulated a 10-year development strategy the Grand Design Initiative, setting a goal of increasing the number of students studying abroad from approximately 500 per year at the time to 1,000 in 10 years, toward the 50th anniversary of our founding in 2020. This initiative aims to achieve the initial goal of 1,000 students studying abroad in 2016, ahead of schedule instead of 2020. Furthermore, we will proceed with the university-wide curriculum being in English, aiming to achieve the language proficiency required for global talent of 480 students.
To achieve these goals, we will work to further improve the international compatibility of our university's overall educational programs through the following six specific projects.
① Develop an undergraduate curriculum with international quality assurance through the expansion of classes taught in foreign languages, the expansion of credit transfer with overseas universities, and the development of dual degree programs.
② Establish and improve a language education system that can produce human resources with internationally accepted foreign language proficiency.
③ Providing more opportunities for overseas learning experiences, such as study abroad, internships, and volunteer work
④ Introduction of a system that makes it easier for students to study abroad for one or more semesters while enrolled, and improvement of the job-hunting support system
⑤ Promote the internationalization of the campus by increasing the number of students with experience studying abroad and international students through improvements to the entrance examination system, educational exchange programs, dormitory facilities, and employment support, as well as by disseminating information in multiple languages.
⑥ Recruiting and training faculty and staff with foreign language skills and overseas experience to support the above efforts
-
Accelerated Program for Reforming University Education
-
2014 "Accelerated Program for Rebuilding University Education" *University-wide
Project implementation period
2014 (September) to 2019 (5 years)
Overview of the initiative
In an age where there are no right answers, there is an urgent need to improve problem-solving AL courses that bridge the classroom and the real world. At the same time, there is a need to develop the ability to accurately grasp a situation and consider one's own response based on that (self-evaluation ability). This initiative aims to increase outside-class study time and improve comprehension by improving the quality of active learning (AL). In addition, it will accelerate the visualization of learning outcomes expected from AL through the development of various evaluation indicators, fostering a culture of evaluation.
This initiative gives both teachers and students an opportunity to reflect on their own efforts in class. This mutual evaluation makes teachers aware that their classes are for the growth of students, and students take responsibility for their own learning. The creation of a school where students can learn actively through friendly competition and grow as human beings is an essential reform for the formation of a "global center for human education," and this initiative is positioned as a major opportunity to promote such reform. Therefore, while introducing AL methods, we will prepare assessment subjects (three assessment gates) whose main function is to measure learning outcomes according to the progress of the grade, and establish a system for checking the extent to which both teachers and students have contributed to achieving the goals of the subject.
One of the educational goals of our university is to encourage learning aimed at creating value that contributes to the peace and prosperity of society, and to cultivate "creative people" who will not stop creating value no matter what difficulties they face. The ability to correctly understand one's own learning process and results and to visualize the future, which will be honed through this initiative, is an essential quality for "creative people" who aspire to contribute to others and society. [Note] The initiative will begin with Faculty of Business Administration as the leading school, and will be expanded to all schools in five years.
-
Top Global University Project
-
Project implementation period
2013-2023
Overview of the initiative
In order to further accelerate the university's efforts to develop global human resources, the university will undertake four projects: "Global Mobility," "Global Learning," "Global Administration," and "Global Core."
First, the "Global Mobility" initiative aims to increase the number of international students and Japanese students studying abroad in order to promote international diversity in the educational environment. Second, the "Global Learning" initiative aims to improve the international compatibility of educational programs. Third, the "Global Administration" initiative aims to promote the globalization of university governance, such as by making university meetings and documents available in English and increasing the proportion of foreign faculty and staff. Fourth, the "Global Core" initiative will establish a "Global Core Center" that will be responsible for promoting globalization in education and research, and will also work to open a "Graduate Graduate School of International Peace Studies" (graduate school) to train highly skilled human resources who will be active in international organizations and global companies.
IR (Institutional Research) activities
Soka University has established the "Soka University IR (Institutional Research) Office" with the aim of improving the quality of education and supporting decision-making regarding its vision. The office is promoting activities to maximize student learning through data-based verification of education and learning outcomes.
IR (Institutional Research) activities
Soka University has established the "Soka University IR (Institutional Research) Office" with the aim of improving the quality of education and supporting decision-making regarding its vision. The office is promoting activities to maximize student learning through data-based verification of education and learning outcomes.
The IR Office mainly handles the following activities:
- Collecting IR data on campus and building a database
- IR activities
- Planning, implementation and result analysis of surveys that contribute to IR, such as student surveys
- President 's Advisory Matters
Learning Report
This report will present the analytical results of learning among Soka University undergraduate students (hereinafter referred to as Soka University students) based on the results of the "Student Life Survey" conducted by our university, with each issue taking a different perspective.
Based on the results of this report, we hope to: 1) create a common understanding of the learning of Soka University students within our university; 2) help the Soka University students who responded to the survey to reflect on themselves and think about their future learning; and 3) inspire their own learning by learning about the learning of other Soka University students.
Related Links
Close
Earthquake-proofing, energy-saving, and power-saving initiatives
We are taking the following steps to improve earthquake resistance, energy efficiency, and power saving.
Earthquake-proofing, energy-saving, and power-saving initiatives
We are taking the following steps to improve earthquake resistance, energy efficiency, and power saving.
Environmental Initiatives
Solar power generation system installed in Global Square
In February 2014, a solar power generation system, the largest of its kind at our university, was installed on the rooftops of the East and West wings of Global Square. The maximum output of electricity is 99kW, and is used to power the building's air conditioning and lighting. A total of 416 crystalline silicon panels have been installed, 208 in each of the East and West wings. This is expected to reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 30 tons per year. A monitor has been installed on the wall of the lounge in front of the Lawson store on the first basement floor of the building, showing the characteristics of the solar power generation system, the amount of power generated and CO2 emissions for that day, and more. It is also useful as an environmental education tool.
Our university installed a 30kW solar power generation system in Lecture Hall Classroom Building in December 2009, and a 37kW solar power generation system in Faculty of Nursing building in February 2013. We will continue to develop environmentally friendly facilities.

Soka University Earthquake Resistance Rate (as of May 1, 2024)
- The earthquake resistance rate of Soka University is 100.0%. [A]
263,205㎡(※①) / 263,205㎡(※②) × 100 = 100.0%
- The earthquake resistance rate of Soka Women’s College is 100.0%. [B]
16,695㎡(※①) / 16,695㎡(※②) × 100 = 100.0%
- The earthquake resistance rate of the Soka University School Corporation is 100.0%. [A+B]
280,404㎡(※①) /280,404㎡(※②) × 100 = 100.0%
*Calculation method is based on the "Survey on the Actual Conditions of Private School Buildings, etc." conducted by the Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan.
*1) Buildings built after July 1, 1981 and before June 30, 1981 that have earthquake resistance.
*②Total floor area
Visualization of energy usage
Soka University compiles the utility costs used on campus each month and presents them in a three-year comparative table. Utility costs are calculated based on the amounts spent on educational facilities such as school buildings, student centers, and student dormitories.
Energy conservation efforts
In order to conserve energy, students, faculty and staff at our university are taking the following measures:
Call to reduce electricity waste
- Students patrol each room from 8:30 p.m. on weekdays to check for unnecessary lighting. A "power saving week" has been set up, and thorough energy saving measures have been called for through announcements in the building.
- The slogan "2UP3DOWN" was posted.
(When traveling between two and three floors, please use the stairs and reduce use of the elevator.) - In rooms used by staff, air conditioning and lighting will be kept to a minimum.
- Converting lighting to LED and thinning out lighting.
- People are urged to keep toilet seats closed when not in use.
Procurement and waste
Procurement and waste
Procurement
Soka University has formulated and regularly updates its "Policy for Promoting the Procurement of Eco-Friendly Goods and Services" in order to prioritize the procurement of environmentally friendly products and services toward achieving carbon neutrality for the university.
About waste
Our university manages waste based on the waste separation guide. We grasp the current status of waste generation and recycling rates, and are implementing the 3R initiative as a concrete measure to reduce waste.
Sorting Guide
Our university is working on "sorting garbage" with the aim of making effective use of resources, increasing recycling rates, and reducing garbage. For rules on sorting garbage on campus excluding dormitories, please refer to "How to sort and put out garbage" and "Soka University garbage sorting dictionary."
Please check the Hachioji City rules regarding garbage sorting in our university dormitories.
For information on the proper disposal of waste generated in connection with educational and research activities at the Faculty of Science Faculty of Science and Engineering, please refer to the "Soka University Faculty of Science and Engineering Waste Disposal Regulations."
Waste Disposal Status and Policy
In accordance with Hachioji City's ordinance on reducing and promoting waste recycling, our university keeps track of the amount of waste generated by the university each year.
General waste generation has been declining year by year, and is projected to be 26% lower in 2023 than the base year (2015). The large decline in general waste generation in 2020 and 2021 is due to reduced facility use due to the impact of infectious diseases. The general waste recycling rate has been increasing year by year, and is projected to be 19.8% higher in 2023 than the base year.
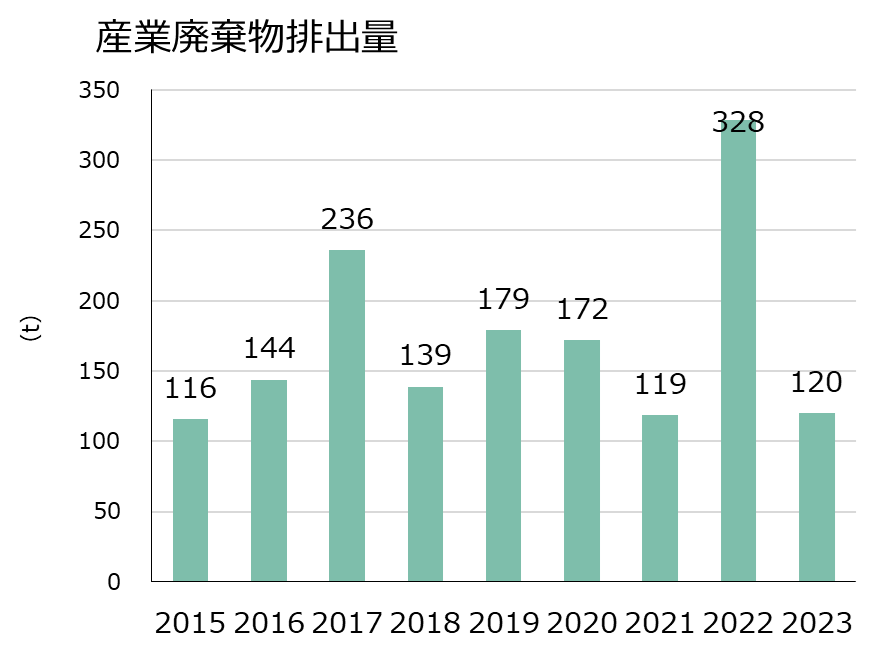
The amount of industrial waste generated varies from year to year due to the effects of demolition work, etc., but the recycling rate has remained high at around 90%, with the exception of some years.
As for general waste, we have implemented initiatives to reduce waste such as collecting mixed paper to encourage the separation of paper and holding book donation events to promote the reuse of books. We will continue to implement initiatives that contribute to reducing waste and improving recycling rates.





About the 3R (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) Initiative
Our university is currently working on 3R-related initiatives as a waste management measure.
◇Reduce (reduce occurrence)
Water server installation
Since the trial introduction in September 2020, we have installed nine water servers for personal bottles on our premises. In terms of PET bottles, this has contributed to a reduction of approximately 34,070 tCO2 from waste per year.

◇Reuse (recycling)
Book presentation ceremony held
We are engaged in activities to provide unneeded library books to faculty, staff, and students, thereby contributing to the reuse of books.

◇Recycling (reuse)
Behavioral awareness poster
Posters encouraging students and staff to separate their garbage are posted on campus to promote behavioral change.

Mixed paper activities implemented
We aim to increase the paper recycling rate by placing dedicated trash bins on campus where students can throw away documents, memos, and other paper items.

Disaster prevention measures
Our university is taking the following steps to prepare for disasters:
Disaster prevention measures
Our university is taking the following steps to prepare for disasters:
Preparing for disasters
- Emergency food stockpile (3,000 people x 3 meals x 3 days)
- Conducting evacuation drills
- Distribution of disaster prevention manuals
- Introduction of a safety confirmation system
- Installation of AED and Evac+Chair (evacuation vehicle for stairs)
The earthquake-resistant storage facility installed in Gymnasium stores three days' worth of emergency food and drink for 3,000 people. In addition, evacuation drills are conducted every May in the male and female student dormitories.
Since 2015, we have been conducting university-wide comprehensive disaster prevention drills every two years, with the participation of students, faculty, and staff. Approximately 5,000 people participated in the drill, which was conducted under the assumption that a major earthquake measuring lower 6 on the Japanese seismic scale had occurred in Hachioji City during classes. Experience corners included a smoke simulation house, rescue from collapsed buildings, water discharge training, an AED experience corner, and an earthquake experience, and students were given hands-on learning opportunities. Disaster prevention education is being provided to ensure the safety of those associated with Soka University in the event of an unexpected major earthquake.
In addition, our university distributes a portable disaster response manual to all students, faculty, and staff regarding initial actions in the event of a disaster. Furthermore, in order to confirm the safety of all students, faculty, and staff in the event of a disaster, we introduced a "safety confirmation system" in October 2011. In the event of a disaster, this system sends a safety confirmation notification to pre-registered personal mobile phones, mobile email, and PC email, and students can report their safety by replying to the notification. Reporting training is also conducted as part of the university-wide comprehensive disaster prevention training.
This system has servers in two locations, Kanto and Kansai, so it can be operated even if a large-scale earthquake occurs in Hachioji City. In addition, the university's own disaster message dial service is now available so that students can contact their families when telephone lines are difficult to connect due to a disaster.
Our university has installed AEDs in 32 locations (including off-site dormitories) and E-vac+Chair (stair evacuation vehicle) in 10 locations, which can be used to carry unconscious or injured people who are unable to walk down stairs.
AED (automated external defibrillator) installation location
Currently, 32 AEDs are installed at Soka University. They are located in the following locations:
Global Square 1F Lobby, Health Center, Central Tower 5F Disaster Prevention Center, Main Gate General Information Desk, Alumni Association Headquarters, Faculty of Faculty of Science and Engineering Building, Faculty of Education Building, Faculty of Nursing Building, Central Library 1F Lobby, Student Hall 1F Entrance, Gymnasium 3F Security Office, Junior College 1F Lobby, Ikeda Auditorium 1F, Taiyo-no-Oka Clubhouse Entrance, World Ground Baseball Club, Matsukaze Center 2F Stairs, Takiyama International Dormitory, Takatomo Dormitory, Tomomitsu Dormitory, Keikan Dormitory, Pioneer Hall, Manyo International Dormitory, Shirahagi Dormitory, Asagiri Dormitory, Koho Dormitory, Sakuraka Dormitory, Soshun Dormitory, Sunflower Hall, Koso Dormitory, Asakaze Dormitory, Koyu Dormitory, Midorikaze Training Camp
Student Initiatives
Our university has a student group called the "Emergency Lifesaving Circle." Founded in 2003, the "Emergency Lifesaving Circle" aims to disseminate knowledge and skills in emergency lifesaving to students, and holds emergency lifesaving seminars on campus several times a year. Students, faculty and staff members of our university who participate in the seminars are certified as "disaster support volunteers" and registered with the Hachioji Fire Department. In the event of a large-scale disaster such as an earthquake or typhoon, cooperation is requested from these registered volunteers through the Hachioji Fire Department when it is deemed necessary for Hachioji City's disaster prevention measures, and they cooperate in disaster prevention activities. This is the first agreement with Hachioji City.
Cooperation with the local community
As part of our cooperation with the local community, our university has designated our First Ground as a "wide-area evacuation site" and has installed guidance signs around the university. In addition, at the request of Hachioji City, the ground has also been designated as a "temporary helicopter landing and takeoff site in the event of a disaster."
In addition, Hachioji City is home to the University Consortium Hachioji, which consists of 23 universities in the city and has concluded a "Mutual Support Agreement for the Supply of Stockpiles of Supplies in the Event of a Disaster." Our university is the representative school of the northern block, and in the event of a disaster, we will work with other universities in the block to set up a support system.
Disaster Response Manual

Smoking is prohibited on all campuses
As of April 2013, smoking has been prohibited throughout the facility.
Smoking is prohibited on all campuses
As of April 2013, smoking has been prohibited throughout the facility.
About the Smoking Cessation Project
Overview of the on-premise smoke-free project

Action Plan
① No smoking allowed anywhere on campus
As of April 2013, smoking has been completely banned on campus. By reducing the smoking environment on campus and taking measures to prevent the increase in new smokers, as well as through cooperation from smokers, we aim to reduce passive smoking to zero and protect the health of all students, faculty and staff.
2) Smoking cessation education
We hold "smoking cessation seminars" for new students and dormitory residents, as well as a "smoking cessation campaign" every April, to help students understand the dangers of tobacco and prevent them from starting to smoke.
3) Support for quitting smoking
We support people who want to quit smoking by providing smoking cessation consultations and smoking cessation seminars with doctors and nurses. We also hold "Smoking Cessation Support Advisor Seminars" for people who want to support others in quitting smoking, and through "Smoking Cessation Supporters" made up of former smokers, we understand and support the difficult task of quitting smoking on your own.
Past efforts
the year of 2000
- Smoking is completely prohibited indoors
2008
- Smoking areas on campus limited to 11 locations to prevent passive smoking
2009
- February: The university council established a committee to consider a university-wide smoking ban.
- July: Smoking cessation counseling begins (for students)
- September: The first "Public Hearing to Consider Smoking Ban at Soka University" was held.
- October: The second "Soka University Public Hearing" was held. The University Council approved the outline of the university-wide smoke-free plan proposed by the study committee (total smoking ban on campus from April 2013).
- November: The Standing Board of Directors approved the above outline. The 3rd "Public Hearing to Consider a Smoking Ban at Soka University" was held.
2010
- January: Establishment of the campus-wide smoke-free committee and promotion office
year 2012
- June: Establishment of the Committee to Promote a Total Smoking Ban on Campus
- September: The university council approved the implementation plan for a complete campus smoking ban.
- October: Notice of removal of smoking areas on campus by the end of March 2013
2013
- April: Smoking ban begins on premises
Smoking cessation consultation
STEP 1 Book your desired date and time
- QR code on the smoking cessation consultation reservation poster or
- アドレス:sotsuensoudan@soka.ac.jp から申し込む
Smoking cessation consultation available hours
Every Monday, Tuesday, and Wednesday (9:30-10:45, 13:00-16:00)
*The first visit will take approximately 1 hour. Follow-up visits will take approximately 30 minutes.
Application details
① Student ID number ② Name ③ Mobile phone number ④ First or repeat visit ⑤ Preferred date and time (up to 3 choices)
STEP 2 Visit the Health Center at the scheduled time.
STEP 3: Receive your "Quit Smoking Diary" at the reception
The smoking cessation diary contains advice for those who want to quit smoking. First, you will fill out the smoking cessation diary questionnaire to check your nicotine dependence level.

STEP 4 Interview with a nurse

STEP 5: Measure CO (carbon monoxide)
Why measure?
This is to measure how much carbon monoxide, one of the 200 harmful substances contained in cigarette smoke, is being absorbed into the body.

STEP 6: Watch a DVD that includes information such as "Why can't I quit smoking?"

STEP 7 Interview with a doctor

STEP 8 Nicotine patches will be prescribed to those who request them (in principle, a one-week supply will be prescribed)



Campus smoking survey report
Since 2009, we have been conducting a smoking questionnaire survey as part of annual health checkups.
We will publish some of the survey results.


