The Kawai Laboratory's brain formation research team published a paper in the research journal Scientific Reports

The Kawai Laboratory and Cerebral Formation Research Team at Soka University Graduate School of Graduate School of Science and Engineering Biosciences Major and Faculty of Science and Engineering Department of Science and Engineering for Sustainable Innovation have discovered the direct effects of methimazole, a drug for hyperthyroidism, on brain formation, and published a paper in the research journal Scientific Reports.
Publication site: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-17482-4
Authors:Akiko So1*, Makoto Nakanishi1. 2, Takahiro Nagayama1, Hironobu Mimori2, Koichi Ikeda1, Hyerian Shin1, §, Hideki Kawai 1,2
1. Soka University Graduate School Graduate School of Science and Engineering Biosciences Major
2. Soka University Faculty of Science and Engineering Department of Science and Engineering for Sustainable Innovation
(Current research institutions: * Department of Bioengineering, Johns Hopkins University, USA, § Dementia Research Group, Korea Brain Research Institute)
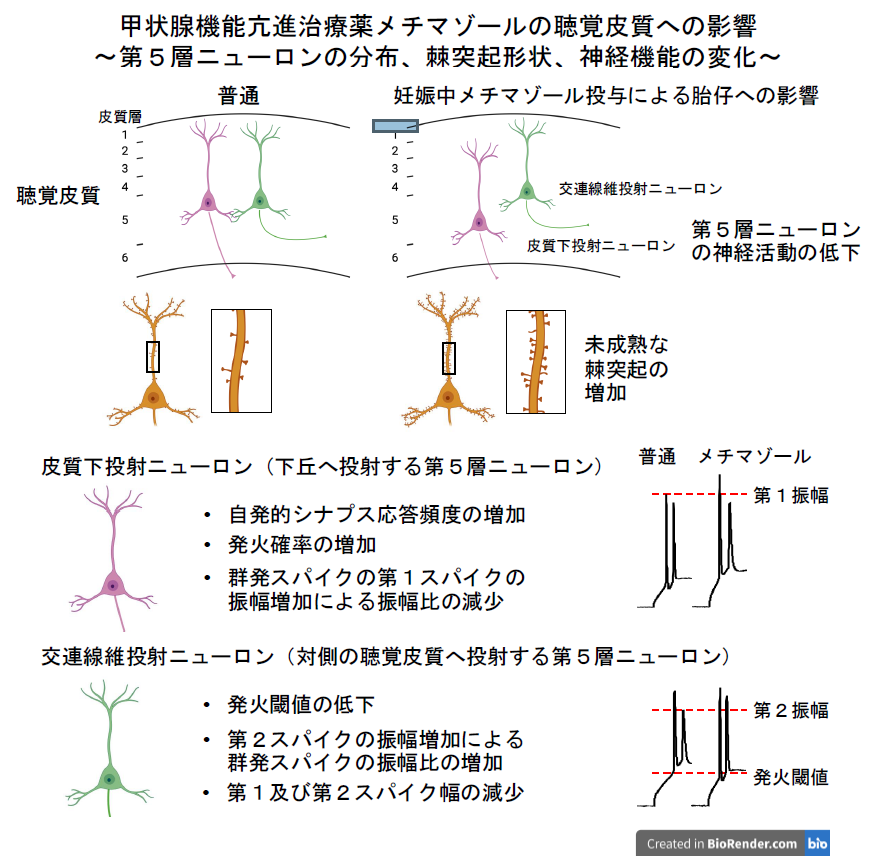
Methimazole (thiazole), a drug used to reduce the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood for hyperthyroidism such as Graves' disease, is used not only in Japan but also around the world. It is recommended to refrain from using this drug during pregnancy because it may cause developmental disorders in the born child by administering this drug during pregnancy. On the other hand, even in pregnant women with hypothyroidism, it was not clear whether the effect of methimazole on the fetus was due to the effect on the blood level of thyroid hormone, as the newborn child developed developmental disorders.
The brain formation research team in Kawai's laboratory found that methimazole affects brain formation even in mice with normal blood levels of thyroid hormone and auditory brainstem response. In particular, in the auditory cortex, abnormal intracortical distribution of fifth-layer efferent neurons and an increase in immature spinous processes seen in developmental disorders were observed. The fifth layer is important for the selection of sound features and the auditory learning of complex sounds such as voices, and there are subcortical projection neurons and compostal fiber projection neurons that are responsible for these. We identified different effects of methimazole on the action potentials of these two types of efferent neurons, and found a decrease in activation in the fifth layer neural circuits including them. These studies suggested that the administration of methimazole in pregnant women directly affects fetal brain formation and causes developmental disorders.


Vice Dean and Professor
Hideki Kawai
- Specialized Field
Neurobiology (neurophysiology, neuropharmacology)
- Research theme
Cerebral formation, function and repair
1) Elucidation of the molecular mechanisms underlying the formation and development of the cerebral neocortex and development of methods to repair developmental abnormalities
2) Elucidation of the mechanism of neural circuit control by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
3) Elucidation of the mechanisms of learning in the brain through experience (e.g., sensory deprivation)
4) Neuroprotection in cerebral infarction and regenerative medicine using stem cells


